Mastering Skills Taxonomy: The Blueprint for Talent Development and Workforce Excellence
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, companies must go beyond merely hiring talent—they need to understand, organize, and develop the precise skills that drive performance. A Skills Taxonomy provides this vital framework, acting as a structured map of competencies that ensures workforce agility, targeted learning, and data-driven talent decisions.
What Is a Skills Taxonomy?
A Skills Taxonomy is a hierarchical classification system that:
Defines individual skills and competencies (both hard and soft)
Groups related skills into categories and subcategories
Maps proficiency levels for each skill (e.g., Beginner → Expert)
By standardizing skill definitions across roles and departments, organizations gain a shared language for talent management.
Why Skills Taxonomy Matters
Alignment with Strategic Goals: Ensures workforce capabilities directly support business objectives.
Enhanced Talent Mobility: Identifies transferable skills for lateral moves or promotions.
Targeted Learning & Development: Pinpoints skill gaps and delivers personalized training paths.
Data-Driven HR Decisions: Enables analytics on skill supply vs. demand, turnover risk, and recruitment needs.
Building Your Skills Taxonomy: Key Steps
Conduct a Skills Audit: Survey current roles, projects, and future business needs.
Define Skill Categories
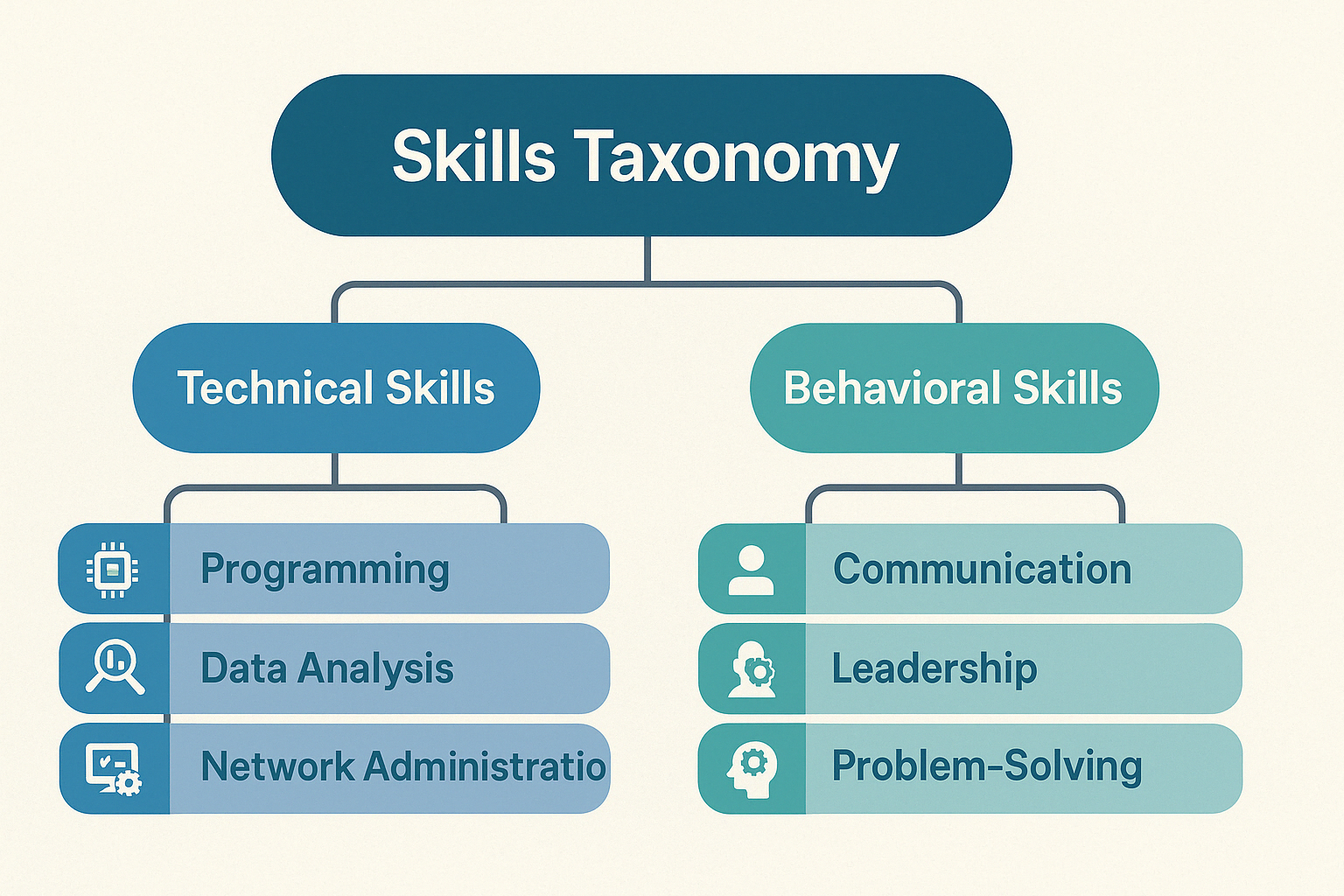
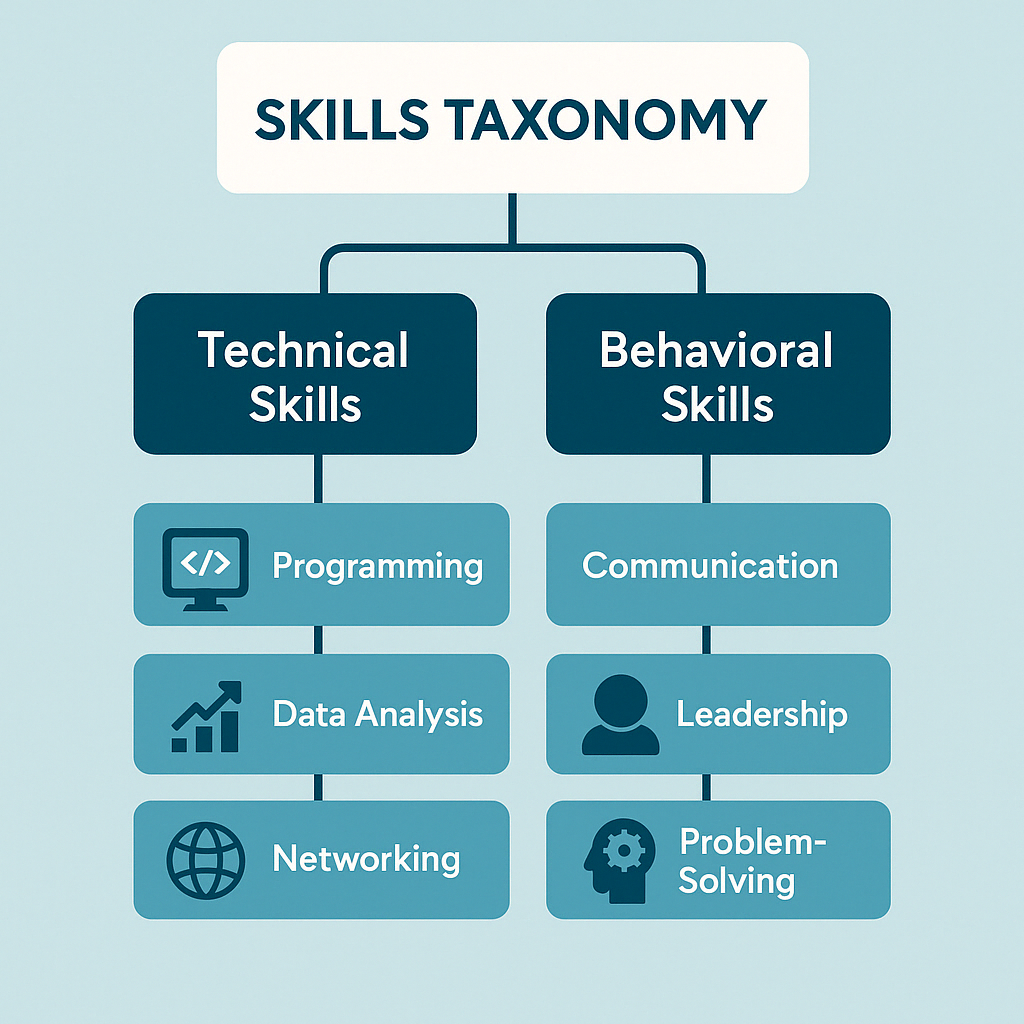
Example hierarchy:
Technical Skills (Programming, Data Analysis, Networking)
Behavioral Skills (Communication, Leadership, Problem-Solving)
Establish Proficiency Levels: Use consistent scales (e.g., 1–5) with clear descriptors.
Validate with Stakeholders: Involve HR business partners, department heads, and frontline employees.
Implement in HR Systems: Integrate taxonomy into ATS, LMS, and performance-management platforms.
Maintain and Update: Review quarterly to add emerging skills (e.g., AI literacy, remote collaboration).
Integrating Skills Taxonomy into HR Processes
Recruitment & Onboarding: Craft job descriptions with taxonomy-approved skill terms.
Learning & Development: Auto-generate personalized learning paths based on skill gaps.
Performance Management: Set clear, taxonomy-aligned objectives.
Succession Planning: Map critical skills to internal talent pools for effective talent mobility.
Leveraging Technology: AI and Digital Platforms
Modern HR platforms now offer:
AI-Driven Skill Extraction from resumes and performance data
Interactive Dashboards for visualizing skill distribution
Skill-Based Talent Marketplaces for agile staffing
Best Practices & Common Pitfalls
Best Practices:
Keep taxonomy lean and user-friendly
Combine employee-driven and leadership-driven inputs
Prioritize change management
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
Neglecting regular updates
Overlooking soft skills
Implementing without clear governance structures
Future Trends in Skills Taxonomy
Continuous Taxonomy Evolution through real-time labor-market intelligence
Adaptive Learning Paths for agile workforce planning
Blockchain-Secured Skill Credentials for transparent verification
Cross-Industry Standardization facilitating talent exchanges
FAQ about Skills Taxonomy
Q1: What is the difference between Skills Taxonomy and Competency Framework?
A Skills Taxonomy typically provides a hierarchical categorization of skills needed within an organization, while a Competency Framework is broader, outlining behaviors, attitudes, and skills required to perform effectively in specific roles.
Q2: How often should a Skills Taxonomy be updated?
Ideally, a Skills Taxonomy should be reviewed quarterly, with major updates annually to accommodate new job roles, emerging skills, or shifts in organizational strategy.
Q3: Can small businesses benefit from a Skills Taxonomy?
Absolutely. Even small businesses benefit from clarifying and structuring skills, leading to improved hiring practices, clearer employee development plans, and better alignment with business goals.
Q4: Who is typically responsible for managing a Skills Taxonomy?
HR or Talent Management teams typically manage Skills Taxonomy, often collaborating closely with departmental leaders to ensure relevance and accuracy.
Related HR Glossary Terms
HR Glossary: Master the Language of Modern HR
Conclusion
A well-designed Skills Taxonomy is more than an HR artifact—it is the strategic backbone for talent optimization. By thoughtfully defining, categorizing, and integrating skills, organizations unlock clearer career pathways, data-rich insights, and a truly agile workforce ready to meet tomorrow’s challenges.
From recruiting candidates to onboarding new team members, MokaHR gives your company everything you need to be great at hiring.
Subscribe for more information

